Uji antagonisme Trichoderma spp. terhadap Ganoderma sp. yang menyerang tanaman sengon secara in vitro
Downloads
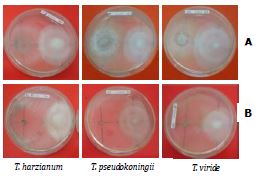
Ganodermasp.adalah cendawan patogen yang dapat menyebabkan penyakit busuk akar pada tanaman sengon (Falcataria mollucana). Ganodermasp. sulit dideteksi karena gejalanyamirip dengan gejala penyakit akar lainnya.Penelitian dilaksanakan di LaboratoriumFakultas Kehutanan IPByang bertujuan untuk mengetahui laju pertumbuhan diameter koloni Ganodermasp. dan Trichodermaspp. dan mempelajari kemampuan Trichoderma spp.dalammenghambat pertumbuhan koloni isolat Ganodermasp. pada media PDA dan MEA secara in vitro. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa pertumbuhan diameter koloni isolat Ganodermasp. pada media PDA (7,09 mm/hari)lebih cepat daripada pertumbuhan pada media MEA (5,41 mm/hari).Laju pertumbuhan diameter koloni isolat Trichodermaspp. pada media PDA diperoleh nilai rata-rata secara berturut-turut yaitu T. viride(69,67 mm/hari), T. harzianum(56,49 mm/hari), dan T. pseudokoningii(42,04 mm/hari). Sedangkan pada media MEA diperoleh nilai rata-rata tertinggi dari pertumbuhan diameter koloni isolat berturut-turut untuk T. pseudokoningii(77,29 mm/hari), T. harzianum(66,50 mm/hari), dan T. viride(59,67 mm/hari). Persentase penghambatan Trichodermaspp.tertinggi ditunjukkan oleh T. harzianum(73,60%) dibandingkanT. pseudokoningii(59,76%), dan T. viride(46,47%).
Abadi, A.L. (1987). Biologi GanodermaboninensePat. Pada Kelapa Sawit (ElaesisguineensisJacg.) dan Pengaruh beberapa Mikroba Tanah Antagonistik terhadap Pertumbuhannya. (Disertasi). Bogor: Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Achmad, S. Hadi, S. Harran, E.S. Gumbira, B.Satiawiharja dan M.K. Kardin. (2010). AktivitasAntagonisme In-Vitro Trichoderma harzianum dan Trichoderma pseudokoningii Terhadap Patogen Lodoh Pinus merkusii. Jurnal Penelitian Hutan Tanaman, 7(5), 233-240.
Achmad, E.N. Herliyana, O.A.F. Yurti dan A.P. Hidayat. (2009). Karakteristik Fisiologi Isolat Pleurotus spp. Jurnal Litri, 15, 46-51.
Agrios,G.N. (1997). Plant Pathology.New York:Academic Press.
Alvarez,P.(2011). Effect of Trichodermaharzianumon Monterey pine seedlings infected by Fusariumcircinatum. Sustainable Forest ManajementResearch Institute. (Thesis). University of Valladolid –INIA.
Amin,F. V.K.Razdan,F.A. Mohiddin,K.A. Bhat and S.Banday.(2010). Potential of Trichodermaspecies as biocontrol agents of soil borne fungalpropagules. Journal of Phytology,2(10),38–41.
Chang, S.T.andP.G. Miles.(1989). Edible Mushrums and their cultivation. Boca Raton: CRC Press.Inc.345 pp.
Cook,R.J.and K.F.Baker. (1989). The Nature on Practice of Biological Control of Plant Pathogens. Minesota:ABS press, The AmericanPhytopathological Society, St. Paul, 539 p
Coșkuntuna,A. and N. Özer.(2007). Biological Control of Onion Rot Disease Using Trichoderma harzianumand Induction of antifungalCompounds in Onion Set Following Seed Treatmen. Departement of Plant Protection, Faculti of Agriculture, Namik Kemal University, Tekirdağ 59030, Turkey,27,330-336.
Haryono, dan S.M. Widyastuti. (2001). Antifungal Activity of Purifieed Endochitinase Produced by Biocontrol Agent TrichodermareeseiAgainst Ganodermaphilippiii. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 4(10), 1232-1234.
Hennssy, C. and A. Daly. (2007). Ganoderma Diseases no. 167. Plant Pathology, Darwin: DiagnosticServices.
Herliyana, E.N. D. Taniwiryono,H. Minarsih, M.A. Firmansayah dan B.Dendang.(2011).Pengendalian Serangan Ganodermaspp. (60-80%) Pada Tanaman Sengon Sebagai Pelindung Tanaman Kopi dan Kakao. Jurnal Ilmu Pertanian Indonesia,16(1), 14-27.
Izzati, N.A. and F. Abdullah. (2008). Disease supressionin Ganoderma - infected oilk palm seedlings treated with Trichoderma harzianum. Plant Protection Science. 44, 101-107.
Kandan, A. R. Bhaskaran and R. Samiyappan. (2010). Ganoderma - a basal stem rot disease of coconut palm in South Asia and Asia Pacific regions. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 43, 1445 – 1449.
Karthikeyan, M, R.Bhaskaran,S.MathiyazhaganandR.Velazhahan.(2007). Influence of phylloplane colonizing biocontrol agents on the black spot of rose caused byDiplocarpon rosae. Journal of Plant Interactions,2(4), 225-231.
Kumar, K., N. Amaresan, S.Bhagat, K.Madhuri andR.C.Srivastava.(2012). Isolation and Characterizationof Trichodermaspp. for Antagonistic ActivityAgainstRoot Rot and Foliar Pathogens. Indian Journal Microbiology,52(2),137–144.
Lee, T.O.Z. Khan, S.G. Kim and Y.H. Kim. (2008). Amendment with peony (Paeonia suffructicosa) root bark powder improves the biocontrol efficacy of Trichoderma harzianum against Rhizoctonia solani. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,18,1537-1543.
Lee,H.M.Z.Khan, S.G Kim, N.I.Baek and Y.H.Kim.(2011). Evaluation of biocontrol potential of some medicinal plant materials alone and in combination with Trichoderma harzianum against Rhizoctonia solani AG 2-1.Journal of Plant Pathology,27,68-77.
López, C.G. V.G. Prieto, S.Lanzuise andS.Lorito.(2014). Enzyme activity of extracellular protein induced in Trichoderma asperellumand T. longibrachiatumby substrates based on Agaricus bisporusand Phymatotrichopsis omnivora. Fungal Biology,118(2), 211-221.
Mile, M. (2003). Tingkat Produktivitas dan KelestarianHutan Rakyat. Prosiding Seminar Sehari, 12 Desember 2003.Prospek Pengembangan Hutan Rakyat di era Otonomi Daerah, Loka Litbang Hutan Monsoon.Badan Litbang Kehutanan. Departemen Kehutanan.
Perazzolli, M. B. Roatti, E. Bozza andI.Pertot.(2011). Trichoderma harzianumT39 induces resistance against downy mildew by priming for defense without costs for grapevine. BiologicalControl,58,74-82.
Purwantisari, S. dan R.B. Hastuti. (2009). Uji Antagonisme Fungi Patogen Phytophthora infestans Penyebab Penyakit Busuk Daun dan Umbi TanamanKentang dengan Menggunakan Trichoderma sp. Isolat Lokal. Jurnal Bioma, 11(1), 24-32.
Rawat, R. and L. Tewari. (2010). Transmission electron microscopic study of the cytological changes in Sclerotium rolfsii parasitized by a biocontrol fungus Trichoderma sp. Mycology: An International Journal on Fungal Biology, 1(4),237-241.
Roatti, B. M. Perazzolli, C.Gessler, andI. Pertot. (2013). Abiotic Stresses Affect Trichoderma harzianumT39-Induced Resistance to Downy Mildew in Grapevine. Phytopathology,103(12), 2013-1233.
Rosa, D.R. and C.J.L. Herrera. (2009). Evaluation of Trichoderma spp. as biocontrol agents against avocado white root rot. Biological Control, 51(1), 66–71.
Schubert, M.S. F.W. Fink and M.R. Schawarze. (2008). Field experiments to evaluate the application of Trichoderma strain (T-15603.1) for biological control of wood decay fungi in tress. Journal of Arboricultural, 31, 249-268.
Shaikh, F.T.andS. Nasreen.(2013). In Vitro Assessment of Antagonistic Activity of T. virideand T. harzianumAgainst Pathogenic Fungi. Indian Journal of Applied Research,3(5),57-59.
Siddiquee, S. U.K. Yusuf, K. Hossain and S. Jahan. (2009). In-vitro studies on the potential Trichoderma harzianum for antagonistic propertiesagainst Ganoderma boninense. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 7(3 and 4), 970-976.
Sinulingga, W. (1989). Pengendalian Biologi Penyakit Cendawan Akar Putih pada Tanaman Karet. Deli Serdang: Pusat Penelitian Perkebunan Sei. Putih, Galang. Hal. 1-7.
Solomon,J.D., T.D.Leininger, A.D.Wilson, R.L.Anderson, L.C.Thompson,and F.I.McCracken. (1993). Ash Pests: A Guide to Major Insect, Diseases, AirPollution Injury and Chemical Injury. Gen. Tech. Rep. SO-96. NewOrleans, LA: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, SouthernForest Experiment Station. 45p.
Sudadi. (2005). Interaksi mineral lempung bahan organik mikroba tanah pengaruh terhadap antagonismedan pemanfaatan dalam pengendalian hayati penyakit tanaman asal tanah. Jurnal Ilmu Tanah dan Lingkungan, 5(1), 8-29.
Supriati, L. I.R. Sastrahidayat dan A.L. Abadi. (2005). Potensi antagonis indigenous lahan gambut dalam mengendalikan penyakit rebah semai (Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc.) pada tanaman kedelai. Jurnal Habitat 15(4), 292-308.
Susanto, A. P.S. Sudharto and R.Y. Purba. (2005). Enhancing biological control of basal stem rot disease (Ganoderma boninense) in oil palm plantations. Mycophatologia, 159, 153-157.
Vinale, F. E.L. Sivasithamparam, R.Ghisalberti, S.L. Marra, Woo andM.Lorito.(2008). Trichoderma–plant–pathogen interactions. Soil Biology andBiochemistry,40,1–10.
Dennis, L.andJ. Webster.(1971). Antagonistic propertiesof species groups of Trichoderma. Production of non-volatile antibiotics. Transactions of the British Mycological Society,57, 25-39.
Yates, I.E. F. Meredith,W. Smart,C.W. Bacon andA.J. Jaworski.(1999). Trichoderma viride suppresses fumonisin B1 production by Fusarium moniliforme. Journal of Food Protection,62(11),1326 –1332.
Widyastuti, S.M. 2007. Peran Trichoderma spp. dalam evitalisasi Kehutanan diIndonesia. Yogyakarta: Gajah MadaUniversity Press, 255p.




