Optimization and Validation of Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Pseudomonas sp. Biofilm Immobilized on Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode in Detecting Benzene
Abstract
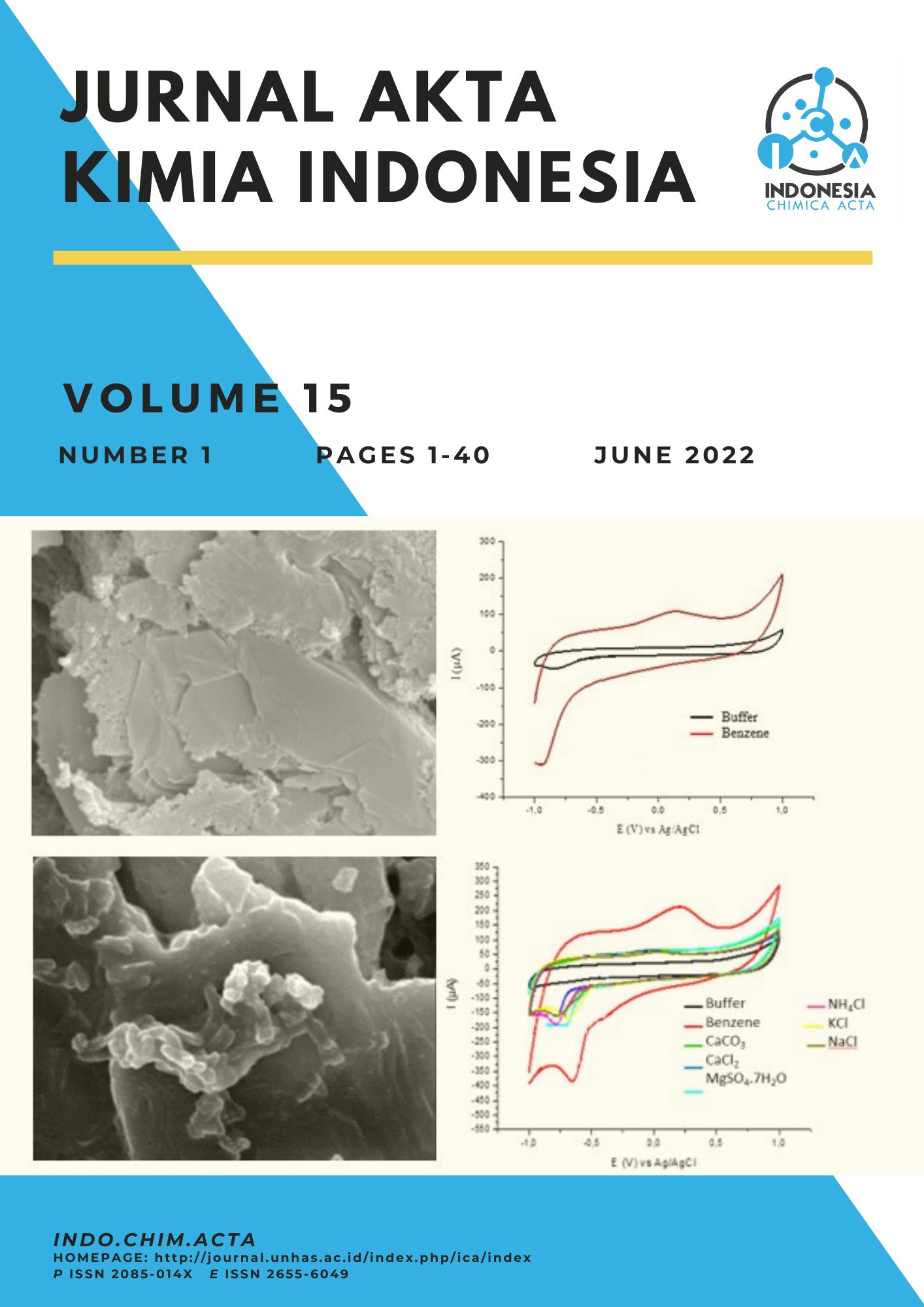
Benzene is known as one of the hazardous compounds potentially interfering the health and polluting the environment. Generally, detecting benzene still requires a long analysis time and expensive costs. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the analytical performance of a biosensor with microbes as the biodetection element. Pseudomonas sp. biofilms which produce benzene dioxygenase enzyme and then immobilized on a Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode (SPCE). The results of the optimization of the biosensor obtained a benzene concentration of 3 mM, a bacterial density of 1.4x1011 cells/mL and suspension pH of 7.5. The optimization results are used to measure the analytical performance of the biosensor. The value of analytical performance produced on linearity is in the measurement range of 0.1 - 3 mM, the equation y = 7.4118x + 80.048 with R2 = 0.9744. The detection limit and quantity limit are 0.5630 mM and 1.8767 mM respectively, with a sensitivity of 7.4188 μA/mM. The precision obtained shows that the SPCE biofilm method has moderate accuracy with a %SBR value below 5%. The selectivity of this method still needs to increase, but the stability of the benzene biosensor increases up to 35 days with an activity of 100.36%. This indicates the immobilization of Pseudomonas sp. had potency as an alternative method for detecting benzene and it can be developed for a prototype.
Full text article
Authors
Copyright (c) 2022 Alfiah Alif, Dyah Iswantini, Henny Purwaningsih, Novik Nurhidayat, Ali Aulia Ghozali, Amalyah Febryanti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This is an open access journal which means that all contents is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.
Jurnal Akta Kimia Indonesia (Indonesia Chimica Acta) operates a CC BY-SA 4.0 © license for journal papers. Copyright remains with the author, but Jurnal Akta Kimia Indonesia (Indonesia Chimica Acta) is licensed to publish the paper, and the author agrees to make the article available with the CC BY-SA 4.0 license. Reproduction as another journal article in whole or in part would be plagiarism. Jurnal Akta Kimia Indonesia (Indonesia Chimica Acta) reserves all rights except those granted in this copyright notice.