Projection of Sea Level Rise Due to Climate Change in Panimbang District Using CMIP6 Model
Main Article Content
Abstract
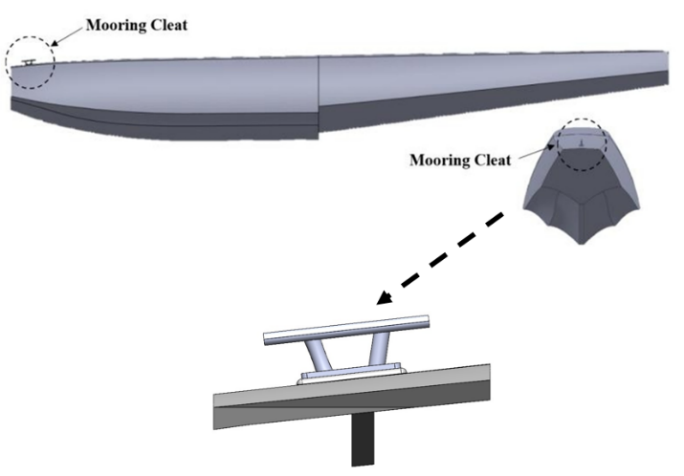
One of the procedures for rescuing a seaplane after an operational is to secure it, namely by mooring at an available port or mooring at a mooring buoy. This mooring buoy is considered a vehicle necessary for securing seaplanes in coastal conditions where it is not yet possible to build infrastructure in the form of an amphiport. To overcome this problem, seaplanes need to add a mooring cleat at the end of the bow of each float, which attaches the rope to the mooring buoy itself. So, it is necessary to study the strength of the mooring cleat itself when withstanding environmental loads. This study was carried out by modelling the mooring cleat using the finite element method to determine where the most significant stresses occur in the mooring cleat structure. Mooring cleats are modelled on deck thickness with varying thicknesses of 20mm and 40mm. The stress that occurred in the mooring cleat structure is then calculated using the Palmgren-Miner rule to determine the fatigue life of the mooring cleat for each variation. It was found that the largest von Misses stress experienced by the structure using 7075-T6 aluminium material was 147.87 MPa, which occurred in the mooring cleat, which was located on the 20mm deck thickness variation at the portside. Meanwhile, this variation's most extended fatigue life calculation occurred for the 40mm deck thickness variation on the portside with 514.43 years.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Allow anyone to modify, improve, and make derivative works, even for commercial purposes, as long as they credit to you for the original work.
References
[1] Baroleh, S. E., Massie, C. D., & Lengkong, N. L. (2023). Implementation of the Paris Agreement International Convention Concerning Climate Change Mitigation in Indonesia. Lex Privatum, 11(5).
[2] IPCC. (2021). IPCC Sixth Assessment Report: The Physical Science Basis. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/.
[3] IPCC. (2018). IPCC Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15/.
[4] IPCC. (2019). Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/
[5] Sung, H. M., Kim, J., Shim, S., Ha, J. C., Byun, Y. H., & Kim, Y. H. (2021). Sea Level Rise Drivers and Projections from Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) under the Paris Climate Targets: Global and around the Korea Peninsula. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(10), 1094.
[6] Reshmidevi, T. V., Kumar, D. N., Mehrotra, R., & Sharma, A. (2018). Estimation of the climate change impact on a catchment water balance using an ensemble of GCMs. Journal of Hydrology, 556, 1192-1204.
[7] Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). (2013). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge University Press.
[8] Hansen, M.C., et al. (2013). High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science, 342(6160), 850-853.
[9] Mujadida, Z., Setiyono, H. , Handoyo, G., Hariyadi, H., & Marwoto, J. (2021). Analysis of sea surface dynamics in the Java Sea using Recurrent Neural Network for the period 1993 to 2019. Indonesian Journal of Oceanography, 3(1), 100-110.
[10] Willis, J. K., Hamlington, B. D., & Fournier, A. (2023). Global mean sea level. NASA. Retrieved January 7, 2025, from https://sealevel.nasa.gov/understanding-sea-level/ key-indicators/global-mean-sea-level Beckley, B., et al. (2017). GMSL dataset. NASA.
[11] IPCC. (2021). Sixth Assessment Report: The Physical Science Basis. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/.
[12] Abidin, H. Z., Andreas, H., Gumilar, I., et al. (2013). Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Natural Hazards, 59(3), 1753–1771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-9866-9.