Impact Analysis Of Implementation Of Bonded Warehouse Policy In Makassar Port New Port On Logistic Costs
Main Article Content
Abstract
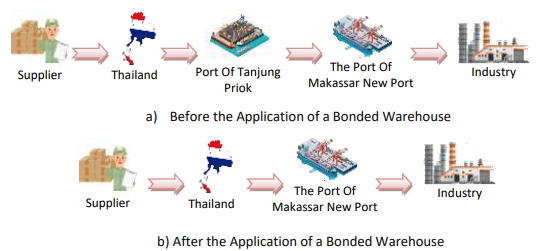
The level of industry dependence on imported goods is still very high while logistics costs in Indonesia reach 24 % of total GDP. Therefore, the need for bonded warehouses to improve logistics management inefficiencies. Bonded warehouse according to PMK RI No. 155/PMK.04/2019 is a Bonded Stockpiling Place (TPB) for stockpiling imported goods, may be accompanied by 1 (one) or more activities in the form of packaging/repackaging, sorting,kitting, packing, setting, cutting, for goods certain goods within a certain period of time to be reissued. The advantages of implementing this bonded warehouse are minimizing the distance between business actors and raw materials so as to reduce dwelling time, make the price of raw materials and production more affordable, obtain exemption or deferral facilities from import duties, excise and taxes. However, some areas with great potential do not have bonded warehouses such as Makassar New Port. The analysis of this study is to compare the logistics costs of importing sugar from Thailand with a bonded warehouse in Tanjung Priok with the implementation of a bonded warehouse in Makassar New Port, which can save costs of Rp. 11,062,648,783. So that the placement of a bonded warehouse in Makassar New Port is the right solution.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Accepted 2022-02-28
Published 2022-02-28
References
S. Hidayat dan H. Palippui, “Analisis Dampak Penerapan Kebijakan Bonded Warehouse (Gudang Berikat) Terhadap Biaya Logistik Di Pelabuhan”, zonalaut, vol. 1, no. 3, hlm. 84-91, Nov 2020.
J. Laksono, and h. Kristiantoro, “determination of the priority selection of the location of the construction of the logistics center bonded based on the aspect of sustainability,” journal of policy analysis and development agency: agency for education and training finance, vol.10, no.1, pp. 51-61, 2017.
Nuryanto, and Ngajian, “range of services. Dwelling time: lower the cost of logistics in the port” in seminar master ppns, vol.3, no.1, pp. 259-264, 2018.
J. Perspektif, t. Selatan," isnsn 2614-283x (online) / isnsn 2620-6757 (print) copyright 707, " steeekan_bar_knan stan. Semua hak yang disediakan, vol.4, tidak. 1, pp. 1-9, 2020
R. Riani, h. Nisyak, and a. Halim, “the factors of cooperation between Indonesia and Thailand in the import of sugar 2014-2018,” Sriwijaya University, 2021.
S. Hidayat and H. Palippui, “Impact Analysis of the Application of Bonded Warehouse Policy on Logistics Costs at the Port”, zonalaut, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 84-91, Nov. 2020.
S. Safrida, s. Sofyan, and a. Taufani, “the impact of the imports of sugar to sugar cane production and domestic sugar prices in Indonesia,” Agricole: journal of agribusiness and social economic of agriculture, Padjadjaran University, vol.5, no.1, pp. 35-48, 2020
R. Triwicaksono, “analysis of the impact of the application of the logistics center bonded to the export of crude palm oil (CPO) Indonesia,” Institut Teknologi Sepuluh November 2018.