Stiffened Plate Analysis by Considering the Effect of Uniaxial Load on FPSO Vessels
Main Article Content
Abstract
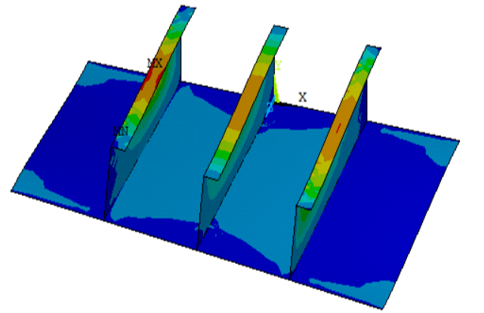
Abstract: Plates are a very important part of shipbuilding and offshore structures. The reinforced plate is used to withstand loads acting in the axial and bending directions. The structure of the deck or bottom plate exhibits buckling or yielding behavior. Thus, it is very important to analyze the ultimate bearing capacity of a plate structure subjected to compressive loads for safe ship structure design. The material configuration used is the most important aspect in the FPSO structure design criteria. Plates and stiffened plates experience local buckling due to the external load when the hull girder collapsed. The objective of the present study is to analyze the effect of flange and web thickness to the ultimate strength on the FPSO in terms of plate deformation located of the bottom and deck area under compression stages. In this study, the attached plate thickness is varied according to FPSO data and BKI Rule. The stiffened plates element located at the bottom and deck area are modelled by Tee-Bar and Angle-Bar element. The simply supported condition is applied to the model and the anon-liniear Finite Element Method is used for the analysis. The result obtained by NLFEM shows that under tension and compression, the stiffened plate of Tee-Bar model, the deformations are 1,75 mm and 1,8 mm respectively. While for Angle-Bar model the deformation are 12,4 mm and 13 mm under compressing respectively.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Accepted 2023-10-28
Published 2023-10-29
References
F. A. Nugroho, B. Siregar, G. L. Putra, and R. Dhelika, “Study on the alteration of geometrical dimensions of tee stiffeners concerning the ultimate strength characteristics under a vertical bending load,” Int. J. Technol., vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 1027–1038, 2018, doi: 10.14716/ijtech.v9i5.1103.
J. Fajrin, Y. Zhuge, F. Bullen, and H. Wang, “The structural behavior of hybrid structural insulated panels under pure bending load,” Int. J. Technol., vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 777–788, 2017, doi: 10.14716/ijtech.v8i5.861.
M. Z. M. Alie and S. I. Latumahina, “Progressive collapse analysis of the local elements and ultimate strength of a Ro-Ro Ship,” Int. J. Technol., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 1065–1074, 2019, doi: 10.14716/ijtech.v10i5.1768.
B. R. Kuriakose and J. John, “Nonlinear Buckling Analysis of Stiffened Plate: A Review,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol., 2022, [Online]. Available: www.irjet.net.
P. T. S and Z. Muis, “ANALISA KELELAHAN STRUKTUR FPSO PT . IRVINE ENGINEERING DUBAI,” no. September, pp. 89–92, 2018.
R. B. P. Sukoco, W. H. A. Putra, and S. H. Sujiatanti, “Analisis Tegangan Pada Penegar Wrang Pelat Akibat Kemiringan Penegar Wrang Pelat,” J. Tek. ITS, vol. 7, no. 2, 2019, doi: 10.12962/j23373539.v7i2.34475.
W. W. Lei Ao, Hao Wu, De-yu Wang, “Evaluation on the residual ultimate strength of stiffened plates with central dent umder longitudinal thrust,” Ocean Eng., vol. 202 107167, 2020.
I. M. Suci et al., “Studi Penelaahan Beberapa Metode Pada Analisis Kekuatan Kapal,” no. 2018, pp. 24–30, 2020.
H. Palippui and S. Ramadhan, “Analysis of The Strength of Barge Structures in the Load Out Offshore Module (Top Side) Process with SPMT”, zonalaut, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1-5, Mar. 2020.
Safitri, M. Z. M. Alie, and T. Rachman, “Analisis kekuatan variasi pelat berpenegar pada dasar kapal fpso dengan kapasitas 370.000 bopd,” no. September, pp. 96–99, 2018.
P. Talia, Juswan, and M. Z. M. Alie, “Analisis deformasi pelat berpenegar pada sekat membujur kapal double hull oil tanker,” no. September, pp. 100–103, 2018.